HDPE vs LDPE- Their Strengths, Weaknesses and Applications
In the vast world of plastics, two titans reign supreme: Low-Density Polyethylene (LDPE) and High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE). Both are incredibly versatile and widely used, but beneath their seemingly similar names lie distinct characteristics that make them ideal for different applications. Today, we delve into the fascinating world of LDPE and HDPE, exploring their properties, strengths, weaknesses, and the real-world applications where they shine.
The Science Behind the Strength:
Both LDPE and HDPE are formed from the polymerization of ethylene gas. However, the way these molecules arrange themselves is what sets them apart.
- LDPE: Here, the long, chain-like polyethylene molecules have numerous branches and side chains. This branching creates a less dense, more flexible structure.
- HDPE: In contrast, HDPE boasts a linear structure with minimal branching. This results in a denser, more rigid material.
A Tale of Two Films: Characteristics of LDPE and HDPE
LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene):
- Characteristics: Flexible, transparent, good impact resistance, waterproof, low melting point, good chemical resistance to some substances (like alcohols).
- Pros: Excellent for applications requiring flexibility and clarity. Easy to process and cost-effective.
- Cons: Lower strength and rigidity compared to HDPE. More susceptible to tearing and puncturing. Can degrade under prolonged UV exposure.
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene):
- Characteristics: Rigid, opaque (can be pigmented), excellent strength and tear resistance, high melting point, good chemical resistance to a wide range of substances.
- Pros: Offers superior strength, durability, and resistance to chemicals and heat. Excellent for long-term outdoor applications.
- Cons: Less flexible than LDPE. Can be more expensive due to its higher density and processing requirements.
The Application Arena: Where LDPE and HDPE Excel
LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene):
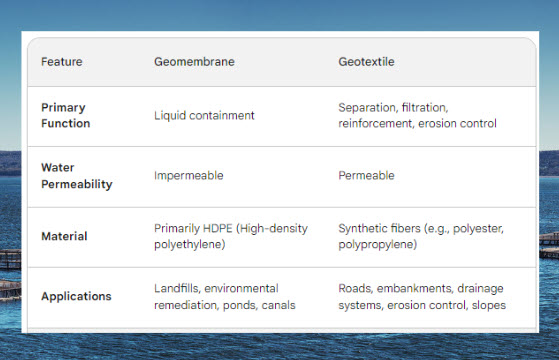
- LDPE geomembranes can be used as temporary covers for construction projects or as secondary liners in landfills, where they provide an additional layer of protection against leaks.
- Grocery Bags: LDPE's flexibility and clarity make it perfect for creating the trusty grocery bags we use daily.
- Squeeze Bottles: Its squeezability makes LDPE ideal for ketchup bottles, laundry detergent containers, and other dispensers.
- Food Packaging: LDPE film wraps our sandwiches, deli meats, and cheese, keeping them fresh and protected.
- Stretch Wrap: LDPE's ability to cling and stretch makes it the champion of securing pallets and boxes during transport.
- Trash Can Liners: LDPE provides a leakproof and tear-resistant barrier for our trash cans.
HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene):
-
Landfills: Due to its high strength, chemical resistance, and low permeability, HDPE geomembranes are widely used as landfill liners. They prevent leachate, a contaminated liquid produced by decomposing waste, from seeping into the surrounding soil and groundwater.
-
Example: The Fresh Kills Landfill in Staten Island, New York, used a multi-layered HDPE geomembrane system to cap the landfill and prevent environmental contamination.
-
Wastewater Treatment Ponds: HDPE geomembranes line wastewater treatment ponds to prevent contamination of the soil and groundwater with untreated wastewater.
-
Example: The East Bay Municipal Utility District (EBMUD) wastewater treatment plant in Oakland, California, uses HDPE geomembranes to line its treatment ponds.
-
Canals and Reservoirs: HDPE geomembranes can be used to line canals and reservoirs to prevent water loss through seepage and prevent contamination of the surrounding soil.
-
Example: The Caracol Copper Mine in Chile uses HDPE geomembrane to line its tailings storage facility, preventing the release of contaminated water into the environment.
- Milk Jugs and Bottles: HDPE's strength and chemical resistance make it the preferred choice for milk containers and other beverage bottles.
- Plastic Lumber: HDPE's rigidity and durability make it a sustainable alternative to wood for decks, fences, and outdoor furniture.
- Cutting Boards: High-density polyethylene offers a non-porous, easy-to-clean surface for chopping and preparing food.
- Pipes and Tubing: HDPE pipes are used for water supply lines, drainage systems, and even gas distribution due to their strength and resistance to corrosion.
- Jerrycans: These sturdy containers, often used for storing chemicals and fuels, rely on HDPE's robust properties.
The Final Verdict: Choosing the Right Champion
The choice between LDPE and HDPE boils down to understanding the specific needs of your application. Here's a quick guide:
- Need flexibility and clarity? LDPE is your champion.
- Prioritizing strength, rigidity, and durability? HDPE takes the crown.
- Cost a major concern? LDPE might be the more budget-friendly option.
- Facing harsh chemicals or extreme temperatures? HDPE offers superior resistance.
Beyond the Basics: A World of Variations
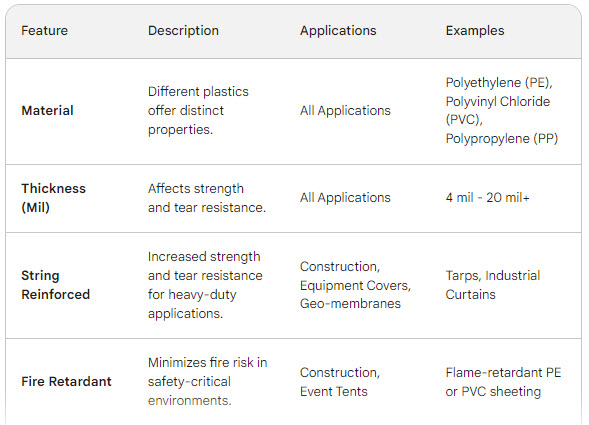
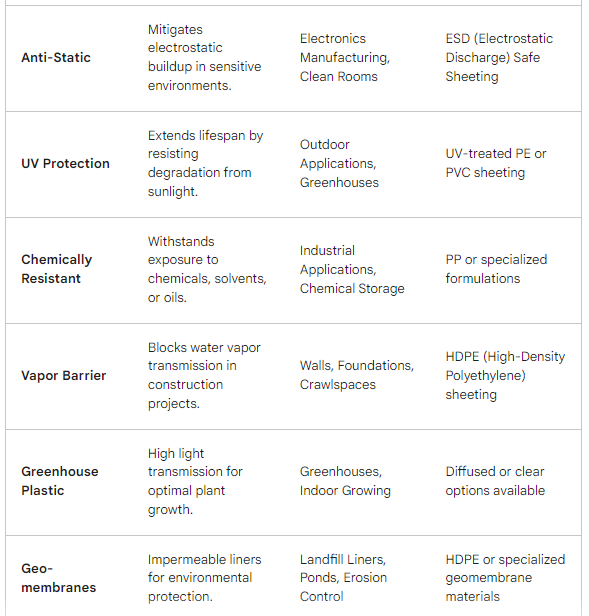
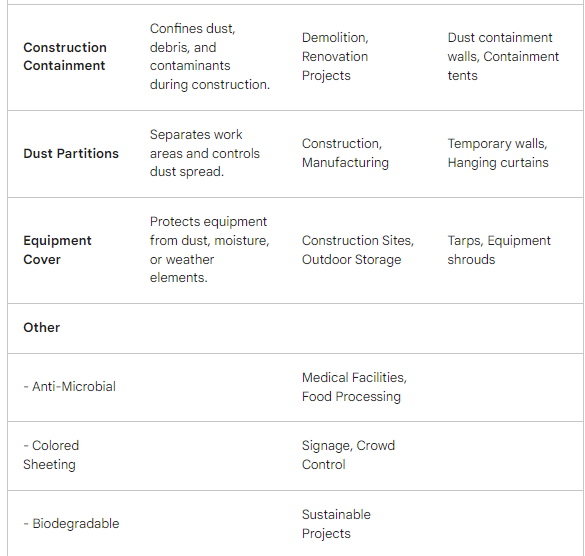
Both LDPE and HDPE can be further modified to enhance specific properties. Additives can be incorporated to improve UV resistance, increase fire retardancy, or enhance color options. Additionally, techniques like crosslinking can create even stronger and more heat-resistant forms of these already versatile materials.
The Takeaway: A Plastic for Every Purpose
LDPE and HDPE are not mere plastic bags – they are the building blocks of countless applications that enrich our daily lives. By understanding their unique properties and strengths, we can make informed choices while appreciating the innovation and versatility these materials offer. So, the next time you reach for a milk jug or squeeze a ketchup bottle, take a moment to acknowledge the silent hero within – LDPE or HDPE, diligently performing its plastic duty!