Demystifying Geosynthetics: Exploring Geomembranes and Geotextiles
In the world of construction and environmental protection, specialized materials play a crucial role in ensuring stability, efficacy, and sustainability. Two such materials, geomembranes and geotextiles, often raise questions about their functionalities and distinctions. This blog aims to demystify these seemingly complex terms by explaining their waterproof nature, highlighting their key differences, and exploring their diverse applications across various sectors.
Unveiling the Waterproof Nature of Geomembranes
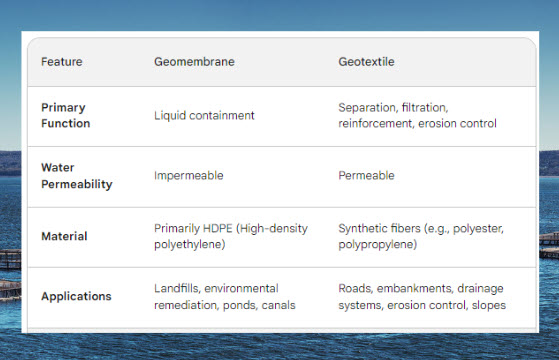
Geomembranes are essentially impermeable liners primarily composed of high-density polyethylene (HDPE). Their primary function lies in preventing the passage of liquids through them. This impermeability arises from the material's dense, continuous structure with minimal to no voids or pores. Additionally, chemical properties of HDPE, such as its inherent hydrophobicity (water-repelling) and chemical resistance, further enhance its ability to effectively block liquids.
While geomembranes are highly effective in preventing liquid permeation, it is important to note that no material can be truly 100% waterproof under extreme circumstances. Factors like prolonged exposure to harsh chemicals, extreme temperatures, or mechanical damage can potentially compromise the long-term waterproof integrity of geomembranes. Nevertheless, with proper installation and maintenance, geomembranes offer an exceptionally reliable solution for applications where liquid containment and control are paramount.
Delving into the World of Geotextiles: Beyond Waterproofing
Geotextiles, unlike geomembranes, are not primarily designed for waterproofing. They are permeable fabrics typically woven or non-woven from synthetic fibers like polyester or polypropylene. Their key functions focus on:
- Separation: Geotextiles act as a barrier that separates different soil layers with varying properties. This prevents intermixing, maintaining the integrity and functionality of each layer in structures like roads, embankments, and drainage systems.
- Filtration: Geotextiles allow the passage of water while retaining soil particles. This facilitates proper drainage and prevents clogging in applications like retaining walls and drainage channels.
- Reinforcement: Certain geotextiles possess high tensile strength, enabling them to reinforce soil and enhance its bearing capacity. This proves valuable in applications like slopes and embankments where stability is crucial.
- Erosion control: Geotextiles can help mitigate soil erosion by acting as a barrier against wind and water forces. This function plays a vital role in protecting slopes, riverbanks, and coastlines.
Unveiling the Diverse Applications of Geomembranes
Geomembranes, due to their exceptional waterproofing capabilities, find application in various sectors:
- Landfills and waste management: Geomembranes act as liners in landfills, preventing leachate (contaminated liquids) from contaminating groundwater and surrounding soil.
- Environmental remediation: Contaminated sites often utilize geomembranes to contain pollutants and prevent their migration into the environment.
- Ponds and canals: Geomembranes serve as impermeable liners for ponds and canals, minimizing water loss through seepage and ensuring efficient water management.
- Aquaculture: Geomembranes are used in pond liners for aquaculture, facilitating controlled and efficient fish and shrimp farming.
- Roof waterproofing: In certain applications, geomembranes serve as waterproof membranes for roofs, offering an additional layer of protection against water ingress.
Exploring the Widespread Uses of Geotextiles
The diverse functionalities of geotextiles translate into a wide range of applications across various industries:
- Roads and pavements: Geotextiles act as separation layers between different layers in road and pavement construction, preventing intermixing and enhancing the overall structure's stability and longevity.
- Embankments and slopes: Geotextiles provide reinforcement and contribute to erosion control on slopes and embankments, ensuring stability and preventing soil erosion.
- Drainage systems: Geotextiles function as filters in drainage systems, allowing water to pass through while retaining soil particles, thereby preventing clogging and facilitating efficient drainage.
Retaining walls: Geotextiles act as drainage channels behind retaining walls, allowing water to drain away from the wall structure, preventing excessive hydrostatic pressure buildup and ensuring stability.
- Construction and civil engineering: Geotextiles find diverse applications in construction and civil engineering projects, including filtration in subdrains, separation layers in landfill covers, and reinforcement in various structures.
- Environmental protection: Geotextiles play a crucial role in environmental protection by aiding in erosion control, preventing soil contamination, and facilitating the creation of sustainable landscapes.
Complementary Roles in Construction and Environmental Projects
It's important to understand that geomembranes and geotextiles often work collaboratively in construction and environmental projects. While geomembranes primarily focus on waterproofing, geotextiles contribute various functionalities like separation, filtration, and reinforcement. Their combined use can create synergistic effects, offering comprehensive solutions for various challenges.
For example, in landfill construction, geomembranes are used as liners to prevent leachate migration, while geotextiles act as drainage layers and separation layers within the landfill cover system. This combined approach ensures both effective containment and proper drainage within the landfill.
Conclusion: Choosing the Right Material for the Job
Understanding the distinct properties and applications of geomembranes and geotextiles empowers individuals to make informed decisions regarding their use in various projects. While geomembranes excel in liquid containment, geotextiles offer diverse functionalities like separation, filtration, reinforcement, and erosion control. Choosing the appropriate material depends on the specific needs of the project and the desired outcome.
By recognizing the distinctive roles and complementary nature of geomembranes and geotextiles, we can leverage their unique capabilities to design and implement efficient, sustainable, and cost-effective solutions acrossvarious sectors, contributing to a more secure and environmentally responsible future.