What is Aquaculture?

Aquaculture, often referred to as fish farming, is the practice of cultivating aquatic organisms such as fish, shellfish, and aquatic plants in controlled environments for commercial or recreational purposes. This comprehensive blog explores the fascinating world of aquaculture, delving into its methods, benefits, and the critical role of tank liners in ensuring sustainable and successful fish farming operations.
1. Understanding Aquaculture:
Aquaculture has emerged as a vital industry globally, providing a sustainable source of seafood to meet the growing demand for fish protein while alleviating pressure on wild fish populations. Fish farming can take place in various settings, including ponds, tanks, cages, and raceways, depending on the species being cultivated and the desired production scale.
2. The Importance of Tank Liners in Aquaculture:
Tank liners play a crucial role in aquaculture operations, providing a protective barrier between the fish and the surrounding environment. A high-quality tank liner creates a controlled aquatic environment that promotes fish health, growth, and overall productivity. Key factors that contribute to the effectiveness of a tank liner include:
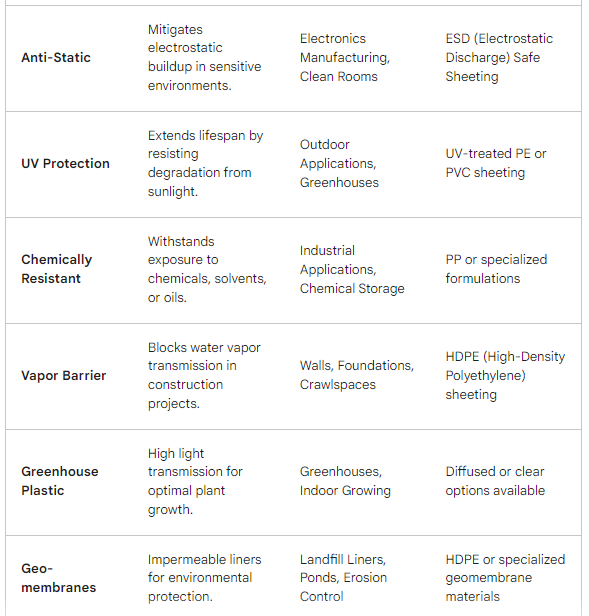
A. Impermeability: A good tank liner should be impermeable to water and gases, preventing leaks and maintaining water quality within the fish tanks. Impermeability is essential for controlling water levels, preventing water loss, and minimizing the risk of contamination from external sources.
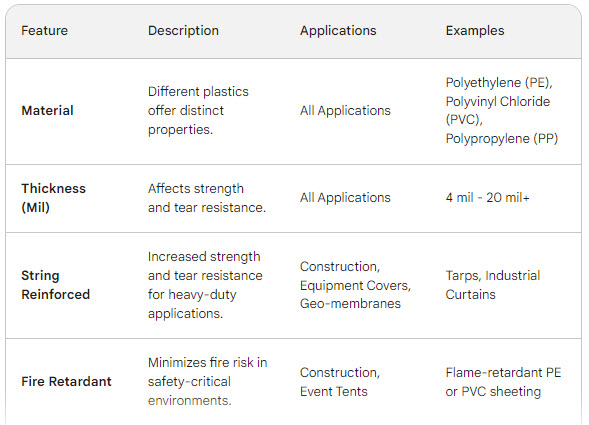
B. Durability: Tank liners must be durable and resistant to punctures, tears, and degradation from exposure to sunlight, chemicals, and biological organisms. Durable tank liners ensure long-term performance and minimize the need for frequent replacements, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
C. Flexibility and Formability: Tank liners should be flexible and formable to adapt to various tank shapes and sizes, including circular, rectangular, and irregular configurations. Flexibility allows for easy installation and ensures a snug fit, minimizing wrinkles and creases that can harbor debris and compromise water quality.
D. UV Stability: UV stability is essential for tank liners installed in outdoor aquaculture facilities exposed to sunlight. UV-stabilized liners resist degradation from UV radiation, ensuring long-term performance and maintaining their structural integrity over time.
E. Biocompatibility: Tank liners should be biocompatible and non-toxic to aquatic organisms, ensuring they do not leach harmful chemicals or substances into the water that could adversely affect fish health and growth. Biocompatible liners support a healthy aquatic ecosystem and contribute to sustainable fish farming practices.
Can You Recommend a Tank Liner?
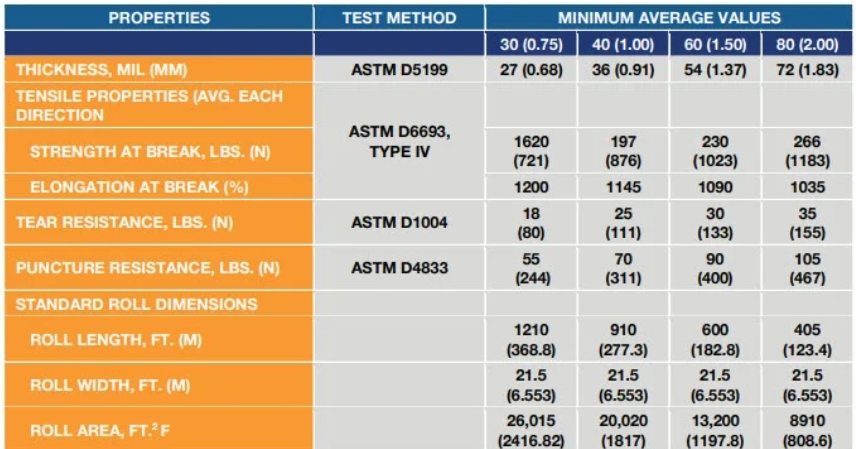
Permalon L20 and L30 are geomembranes manufactured by Reef Industries, primarily used for lining applications in various industries such as environmental containment, agriculture, mining, and aquaculture. These geomembranes are highly sought after by professionals and organizations requiring reliable containment solutions due to their exceptional durability, chemical resistance, and impermeability.
The viability of Permalon L20 and L30 lies in their ability to provide long-term protection against leaks, seepage, and environmental contamination. Both variants offer robust construction and high tensile strength, making them suitable for demanding applications where durability is essential. Permalon L20 is a 20 mil (0.5 mm) thick geomembrane, while Permalon L30 is a 30 mil (0.75 mm) thick geomembrane, providing options for varying project requirements and site conditions.
Organizations involved in environmental containment projects, such as landfill construction, wastewater treatment facilities, and hazardous waste storage sites, often purchase Permalon L20 and L30 geomembranes. These geomembranes are preferred for their ability to create impermeable barriers that prevent the migration of contaminants into the soil and groundwater, thus safeguarding the environment and public health.
Furthermore, Permalon L20 and L30 find applications in aquaculture for pond lining, mining for tailings containment, agricultural water storage, and industrial chemical containment. Their versatility and adaptability to different environments make them a preferred choice for professionals seeking reliable geomembrane solutions.
What makes Permalon L20 and L30 special is their combination of durability, chemical resistance, and impermeability, which ensure long-term performance and reliability in demanding applications. Additionally, their ease of installation and customization options make them suitable for a wide range of projects, from small-scale pond liners to large-scale environmental containment systems. Overall, Permalon L20 and L30 geomembranes offer a cost-effective and sustainable solution for protecting the environment and ensuring the integrity of containment structures in various industries.
3. Applications of Tank Liners in Aquaculture:
Tank liners are utilized in various aquaculture systems and facilities, including:
A. Recirculating Aquaculture Systems (RAS): RAS utilize tank liners to create closed-loop systems that recirculate and filter water, maximizing water efficiency and minimizing environmental impact. Tank liners play a crucial role in maintaining water quality and facilitating efficient filtration and water treatment processes.
B. Aquaponics Systems: Aquaponics systems combine aquaculture (fish farming) with hydroponics (soilless plant cultivation) in a symbiotic ecosystem. Tank liners are used in aquaponics tanks to contain fish and nutrient-rich water, supporting the growth of plants without soil and facilitating nutrient cycling between fish and plants.
C. Hatcheries and Nurseries: Fish hatcheries and nurseries utilize tank liners to rear juvenile fish in controlled environments before transferring them to larger grow-out tanks or ponds. Tank liners in hatcheries provide a clean and controlled environment that promotes optimal growth and survival rates for young fish.
D. Fish Holding Tanks: Tank liners are used in fish holding tanks for temporary storage, transportation, and quarantine purposes. Liners in holding tanks ensure fish are housed in a safe and controlled environment during handling, shipping, and acclimation processes.
4. Conclusion: Embracing Sustainable Aquaculture Practices
In conclusion, aquaculture represents a vital and growing industry that plays a crucial role in meeting global demand for seafood while promoting sustainability and environmental stewardship. Tank liners are essential components of aquaculture systems, providing a protective barrier that creates controlled aquatic environments conducive to fish health and growth. By investing in high-quality tank liners that meet the criteria of impermeability, durability, flexibility, UV stability, and biocompatibility, fish farmers can ensure the success and sustainability of their aquaculture operations. As the aquaculture industry continues to evolve, embracing innovative technologies and sustainable practices will be key to meeting the growing demand for seafood while minimizing environmental impact and supporting healthy aquatic ecosystems.