HDPE and LDPE- What's the difference?
HDPE and LDPE, both common plastics, can leave you wondering: what's the difference? Here's a quick breakdown:
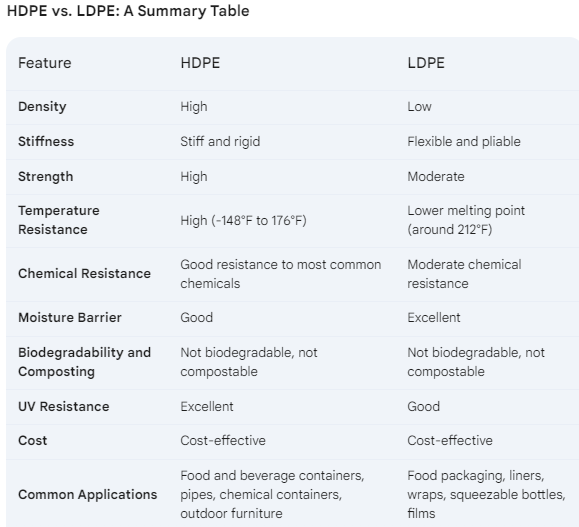
- HDPE (High-Density Polyethylene): Strong, rigid, and moisture-resistant. Ideal for pipes, containers, and outdoor furniture.
- LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene): Flexible, good moisture barrier. Perfect for food packaging, wraps, and squeezable bottles.
Key Differences: Consider stiffness (HDPE is stiff, LDPE is flexible) and temperature resistance (HDPE tolerates higher temperatures).
Choosing the Right Plastic: For strength and rigidity, choose HDPE. For flexibility and moisture control, opt for LDPE.
HDPE vs. LDPE: Decoding the Plastic Alphabet Soup
High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) is a workhorse plastic material with a well-deserved reputation for durability, cost-effectiveness, and moisture resistance. However, like any material, HDPE has its limitations. Let's delve deeper into the world of HDPE, exploring its strengths, weaknesses, and where its cousin, LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene), might be a better fit.
The "Con" Perspective of HDPE:
- High Flammability: HDPE has a higher flammability rating compared to some other plastics. For applications requiring flame retardancy, other options like flame-retardant HDPE blends or entirely different materials might be necessary.
- Stress Cracking: HDPE can be susceptible to stress cracking, especially under prolonged strain or exposure to certain chemicals. In such cases, materials with higher stress-cracking resistance might be needed.
- Biodegradability and Composting: HDPE is not biodegradable and cannot be composted. If these qualities are crucial for your application, consider biodegradable alternatives.
- Oxidizing Acids and Chlorinated Hydrocarbons: HDPE has limited resistance to oxidizing acids and chlorinated hydrocarbons. For applications involving these chemicals, alternative plastics with better chemical resistance would be a safer choice.
- Thermal Expansion: HDPE has a higher coefficient of thermal expansion compared to some other plastics. In situations where dimensional stability under fluctuating temperatures is critical, a material with lower thermal expansion might be preferable.
The Power of HDPE: Advantages and Applications
Despite the limitations mentioned above, HDPE boasts numerous advantages that make it a popular choice:
- Cost-Effective: HDPE is a relatively inexpensive plastic, making it a budget-friendly option for various applications.
- Temperature Resistance: HDPE can withstand a wide range of temperatures, from -148°F to 176°F, making it suitable for various environments.
- Non-Leaching and UV Resistant: HDPE is non-leaching, meaning it doesn't release harmful chemicals, and it's resistant to UV degradation, ideal for long-lasting outdoor applications.
- Chemical Resistance: HDPE offers good resistance to most common household and industrial chemicals.
- Stiff Material: The high density of HDPE translates to a stiff and strong material, perfect for applications requiring structural integrity.
Common Uses of HDPE:
- Food and Beverage Containers: HDPE's blow-molding properties and durability make it ideal for water bottles, milk jugs, and other food-safe containers. Here, LDPE can also be a suitable option, especially for applications requiring more flexibility, like squeezable bottles. LDPE is generally considered safe for food contact as well.
- Chemical Containers: HDPE's chemical resistance makes it a great choice for laundry detergent bottles, motor oil containers, and other chemical storage applications. However, for particularly harsh chemicals, even HDPE might not be suitable. In those cases, industrial-grade containers designed for specific chemicals would be necessary.
- Pipes and Outdoor Applications: HDPE pipes are popular for their durability, UV resistance, and ability to withstand freezing temperatures. LDPE, due to its lower melting point and overall strength, wouldn't be a suitable option here.
- Toys: HDPE's durability and UV resistance make it a good choice for some types of toys. However, for softer and more flexible toys, LDPE is often preferred.
Is HDPE Eco-Friendly?
Compared to some other materials, HDPE production requires less energy. Additionally, HDPE is often recyclable (check for recycling symbols on the product), making it a more sustainable option in the long run.
Beyond HDPE: Considering LDPE
While HDPE excels in strength and durability, LDPE (Low-Density Polyethylene) offers a different set of advantages:
- Flexibility: LDPE is known for its flexibility, making it ideal for applications requiring a softer, more pliable material. For example, LDPE is commonly used in food wraps and squeezable bottles.
- Moisture Barrier: LDPE is a good moisture barrier, making it suitable for applications like food packaging and liners.
- Cost-Effective: Similar to HDPE, LDPE is a relatively inexpensive plastic.
Choosing the Right Material: HDPE vs. LDPE
The best choice between HDPE and LDPE depends on your specific application. Here's a quick guideline:
- Need a strong, rigid, and moisture-resistant material? HDPE is your go-to choice
Conclusion
HDPE is a versatile and reliable plastic, offering a winning combination of strength, durability, and affordability. However, its limitations in flexibility, biodegradability, and specific chemical resistance require consideration. When these limitations become dealbreakers, LDPE emerges as a strong alternative, particularly if flexibility and a good moisture barrier are priorities.
By understanding the strengths and weaknesses of both HDPE and LDPE, you can make informed decisions and choose the right plastic material for your project.
Ready to Explore the World of HDPE and LDPE?
Global Plastic Sheeting offers a wide range of HDPE and LDPE products to meet your specific needs. Contact us today to discuss your project and find the perfect plastic solution!


